Introduction
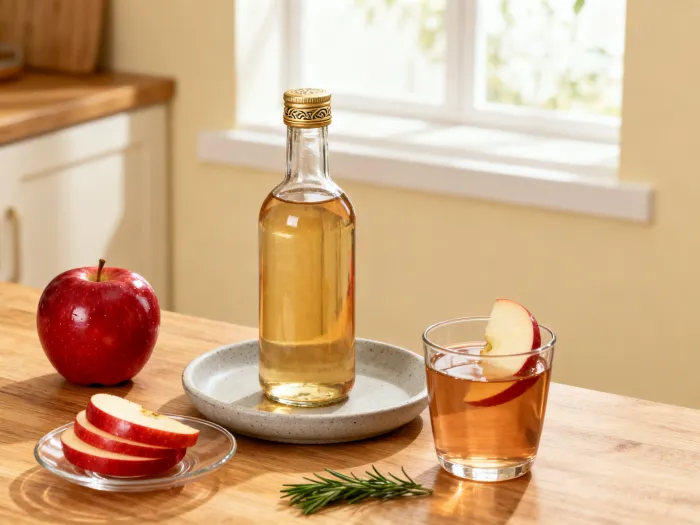
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has long been hailed as a versatile health elixir, known for its ability to aid digestion, boost immunity, and support overall wellness. However, like any health supplement, its benefits are maximized only when consumed correctly. Misuse or excessive intake can lead to adverse effects, making it essential to understand the proper methods of consumption.
Health Benefits of Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is rich in acetic acid, which is believed to provide several health benefits. Among its most notable advantages are:
- Improved Digestion: ACV helps stimulate digestive enzymes, aiding in the breakdown of food and enhancing nutrient absorption.
- Immune System Support: Its antimicrobial properties may help combat harmful bacteria and viruses.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Studies suggest that ACV can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels after meals.
- Weight Management: Some research indicates that ACV may increase feelings of fullness, potentially reducing calorie intake.
- Skin Health: When diluted and applied topically, ACV may help balance skin pH and reduce acne-causing bacteria.
While these benefits make ACV an appealing addition to a healthy lifestyle, overconsumption or improper use can lead to issues such as tooth enamel erosion, digestive discomfort, or interactions with medications.
The Correct Way to Consume Apple Cider Vinegar
1. Dilution is Key
Apple cider vinegar is highly acidic and should never be consumed undiluted. To minimize its impact on the stomach lining and teeth enamel, mix 1-2 tablespoons of ACV with at least 8 ounces (240 ml) of water. Adding a teaspoon of honey can further reduce acidity while enhancing flavor.
2. Optimal Timing
For best results:
- Before Meals: Drinking ACV 20-30 minutes before meals can stimulate digestive enzymes and prepare your stomach for food intake.
- Morning Routine: Consuming it on an empty stomach in the morning may kickstart digestion and provide a gentle detoxifying effect.
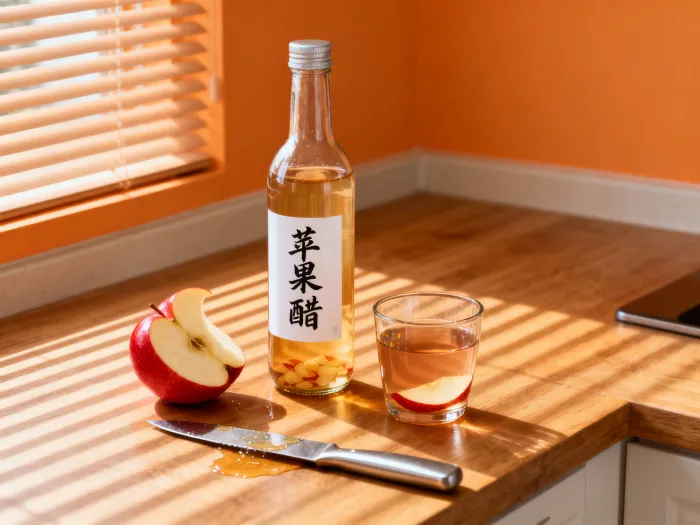

3. Moderation Matters
Excessive intake of apple cider vinegar can lead to side effects such as low potassium levels or weakened bones over time due to its acidic nature. Limit consumption to no more than 2 tablespoons per day.
4. Use with Caution for Sensitive Individuals
People with certain medical conditions—such as acid reflux or ulcers—should consult their healthcare provider before incorporating ACV into their diet. Pregnant women and individuals taking medications for diabetes or heart disease should also exercise caution due to potential interactions.
Additional Tips for Safe Usage
- Drink Through a Straw: To protect your teeth from acid erosion, use a straw when drinking ACV mixtures.
- Rinse Your Mouth Afterward: Follow up with water or rinse your mouth after consuming ACV to prevent damage to tooth enamel.
- Choose Quality Products: Opt for organic, unfiltered apple cider vinegar labeled “with the mother,” which contains beneficial enzymes and probiotics.
- Incorporate into Recipes: Instead of drinking it directly, consider using ACV as an ingredient in salad dressings, marinades, or smoothies for added flavor and health benefits.
Conclusion
Apple cider vinegar can be a valuable addition to your health regimen when consumed thoughtfully and responsibly. By diluting it with water or honey, timing consumption appropriately, and adhering to recommended daily limits, you can enjoy its numerous health benefits while minimizing potential risks. As with any dietary supplement, consult your healthcare provider before making significant changes to your routine.
When used correctly, apple cider vinegar is not just a trend but a timeless remedy that continues to support wellness across generations.