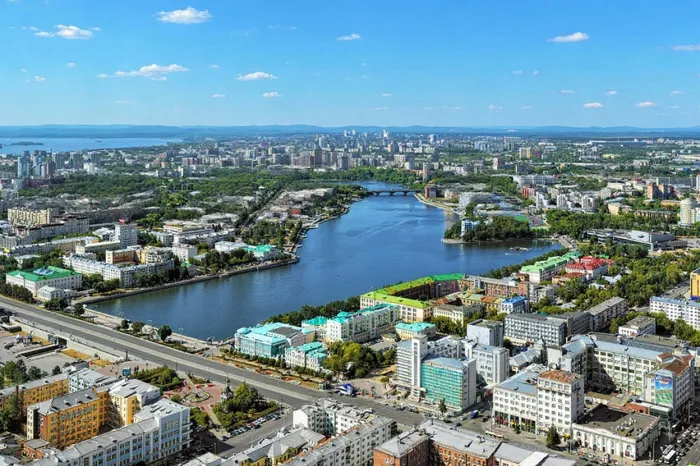
The eagerly predicted microchip manufacturing facility in Yekaterinburg, Russia, will now no longer start operation till 2027, signaling a first-rate setback withinside the u . s . a .’s efforts to reinforce its home semiconductor industry. Announced as a important pillar of Russia’s approach to improve its technological and monetary sovereignty, the put off has dampened hopes for a speedy acceleration of microchip manufacturing.
The plant, placed withinside the coronary heart of Russia’s Ural region, become in the beginning predicted to release in advance however has been driven returned with the aid of using numerous years. This improvement underscores the continual demanding situations going through Russia’s microelectronics quarter, which has struggled to hold tempo with worldwide advances and home ambitions. The postponement is specially massive as Russia seeks to lessen reliance on imports for essential high-tech additives amid heightened worldwide tensions and deliver chain uncertainties.
Industry observers factor out that the put off should have extensive implications for Russian producers who rely upon specialised microchips for his or her products. The authorities has again and again emphasised the significance of homegrown chip manufacturing as a part of country wide protection and monetary resilience plans. With the Yekaterinburg plant’s release now set for 2027, neighborhood organizations and tech builders will retain relying on overseas providers longer than predicted.
Experts acquainted with the state of affairs endorse that a aggregate of technical, financial, and geopolitical boundaries contributed to the revised timeline. Producing semiconductors is technologically complicated and capital-intensive, frequently requiring specialised machinery, skilled engineers, and seamless get right of entry to to worldwide markets—all elements that can have demonstrated tough beneathneath modern-day conditions. The Russian semiconductor quarter has confronted deliver chain disruptions, regulations at the import of equipment, and barriers on get right of entry to to worldwide highbrow property.
For the metropolis of Yekaterinburg, hopes of turning into a era hub at the moment are positioned on hold. Local officers had championed the microchip plant as a supply of professional jobs and nearby investment. Instead, the put off leaves uncertainty across the broader monetary blessings and the introduction of a high-tech surroundings withinside the region. It additionally increases questions on whether or not comparable tasks throughout the u . s . a . will meet introduced timelines, or if wider delays may be predicted.
Despite the setback, government continue to be devoted to accomplishing technological self-sufficiency. Government spokespeople retain to voice self assurance that the Yekaterinburg facility will play a key function in destiny Russian microelectronics as soon as operational. In the meantime, the put off serves as a reminder of the complexities going through international locations pursuing home semiconductor talents in a aggressive and frequently unpredictable worldwide environment.
As 2027 approaches, enterprise contributors and policymakers alike will watch intently to peer if the Yekaterinburg venture subsequently can provide on its promise—or if similarly postponements are across the corner.